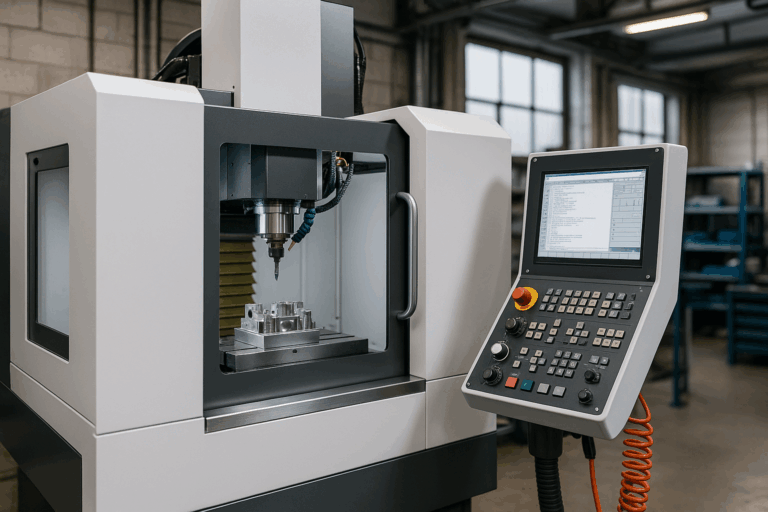
If you’re looking to boost your business’s manufacturing potential, understanding what a CNC machine can do is the first step. These machines are capable of performing a wide range of operations with precision and efficiency.
From milling and turning to drilling and cutting, each type of CNC machine offers unique capabilities that can transform your production line. In this article, we’ll explore how many operations a CNC machine can perform and help you find the perfect one for your business needs.
What Are CNC Machine Operations?
CNC machine operations refer to the specific tasks that a computer-controlled machine can perform, such as cutting, drilling, milling, or turning. Each operation involves precise movements programmed through CAD/CAM software to shape or modify materials with exceptional accuracy. Understanding these operations is essential to choosing the right CNC system for your production goals
Basic CNC Processes: Cutting, Drilling, Milling, and More
Understanding the main types of CNC operations is key to grasping how computer-controlled machining works. Below is an overview of the most common processes:
- CNC Drilling. This process uses a drill bit to create precise holes in the workpiece. CNC drilling machines are often combined with other systems and are typically used for making holes for screws or decorative purposes.
- CNC Milling. In milling, a rotating cutting tool removes material from a stationary workpiece. Mills can operate on multiple axes and use various tools, allowing for techniques like end, face, or slab milling depending on the project’s needs.
- CNC Turning. Turning involves rotating the workpiece while a fixed cutting tool shapes it. It’s mainly used for cylindrical components, such as shafts or turbine parts.
- CNC Routing. Routing cuts through materials by moving the tool across the surface and through its depth, dividing the piece into sections. It’s commonly used for woodworking and lightweight materials.
- CNC Grinding. Grinding smooths the surface of a workpiece using abrasive wheels, removing tiny amounts of material to achieve a refined finish or correct minor imperfections from previous processes.
Beyond the main CNC processes, several other specialized techniques are also widely used. CNC broaching shapes keyways and profiles with a toothed tool, while plasma and laser cutting use high-energy jets for precise metal and material cuts. Water jet cutting offers a cold-cutting alternative that works on almost any material. For surface finishing, honing and lapping refine parts with extreme accuracy using abrasive tools or pastes.
Automated Precision: The Power of CNC Programming
CNC programming is the process of creating digital instructions that guide machine tools to cut, move, and shape materials with precision. It usually starts from a CAD design, which is converted into CAM software to generate G-code and M-code, the commands that control tool paths and machine functions. In simple terms, it’s what turns a digital model into a perfectly manufactured part.
CNC programming brings plenty of benefits to modern manufacturing. Because it follows exact digital instructions, it eliminates human error and delivers outstanding precision, something especially important in fields like aerospace or medical equipment production. Every part comes out exactly the same, ensuring consistent quality even in large production runs. Automation also saves time and reduces manual work, while any design change can be made quickly by simply updating the software. CNC machines can handle many different materials, from metals like aluminum and steel to various plastics, making them incredibly versatile.
How to Choose the Right CNC Machine Based on Operations
When choosing the right CNC machine for your operations, the first step is to clearly define your production needs. Think about the materials you’ll be working with, whether it’s wood, plastic, aluminum, or steel, as this will determine the machine’s required spindle power, torque, and rigidity. You should also consider the complexity of your parts: simple shapes can be handled by basic models, while intricate designs or tight tolerances may require a multi-axis CNC system.
Once you’ve identified your needs, it’s time to select the right machine type. A CNC lathe is perfect for cylindrical parts, a milling machine excels at creating detailed 3D components, and a router works best with softer materials like wood or foam. For metal fabrication, a plasma cutter can deliver clean, precise cuts.
Finally, evaluate the machine’s technical specifications and practical aspects. Make sure it offers the right size and cutting capacity for your projects, reliable precision and repeatability, and a control system compatible with your design software. Don’t forget to factor in the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, tooling, and energy consumption.
In short, CNC machines can perform a wide variety of operations with precision and consistency. Understanding what each process offers helps you choose the machine that best fits your materials, production goals, and budget. The right CNC system will not only improve efficiency but also take your business to the next level.
If you’re interested in learning more, explore this section of our blog for related articles and insights https://3axis-group.com/cnc-lathe-performanc